一、chrony概述
chrony是一款开源的NTP时间同步软件,被广泛应用于unix-like操作系统(比如Linux、BSD和macos)以提供高精度的时间同步服务。该软件专注于性能和可靠性,在时间同步中具有低延迟、低CPU占用率和低内存消耗等优势。chrony由两个关键组件组成,分别是chronyd(服务器端)和chronyc(客户端)。
- chronyd:作为一个后台运行的守护进程,负责调整系统时钟并与时钟服务器同步,它通过平滑调整计算机的时钟增减速率来确保时间的准确性。
- chronyc:提供用户友好的界面,用于监控性能指标和灵活配置。它可在与chronyd实例相同的计算机上运行,也可以在远程计算机上运行以进行相关操作。
二、实验环境
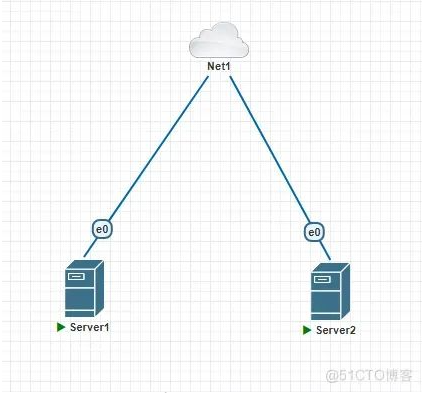
2.1 实验拓扑
如图,两台服务器Server1、Server2连接到同一网络
2.2 本地环境规划
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 操作系统版本 | 内核版本 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Server1 | 172.16.0.134/24 | Rocky Linux 8.9 (Green Obsidian) | Linux 4.18.0-513.5.1.el8_9.x86_64 |
| Server2 | 172.16.0.150/24 | Rocky Linux 8.9 (Green Obsidian) | Linux 4.18.0-513.5.1.el8_9.x86_64 |
Net1网络中配置了NAT(网络地址转换),两台服务器均可以访问公网
三、配置时间同步
3.1 安装chrony
[root@Server1 ~]# rpm -qa | grep chrony chrony-4.2-1.el8.rocky.1.0.x86_64
Rokcy Linux 8.9版本默认安装了chrony,验证安装状态:
3.2 配置Server1从公网时间源服务器同步时间
编辑“/etc/chrony.conf”文件:
[root@Server1 ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf # Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project. # Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html). # pool 2.rocky.pool.ntp.org iburst # 注释该行,添加如下两行,理论上想添加多少时间服务器都可以 Server ntp.aliyun.com iburst # 阿里时间源服务器 Server time1.cloud.tencent.com iburst # 腾讯时间源服务器
重启chronyd服务,并设置开机自启:
[root@Server1 ~]# systemctl restart chronyd [root@Server1 ~]# systemctl enable chronyd [root@Server1 ~]# systemctl is-active chronyd # 查看chronyd服务是否正常运行 active [root@Server1 ~]#
查看时间同步状态:
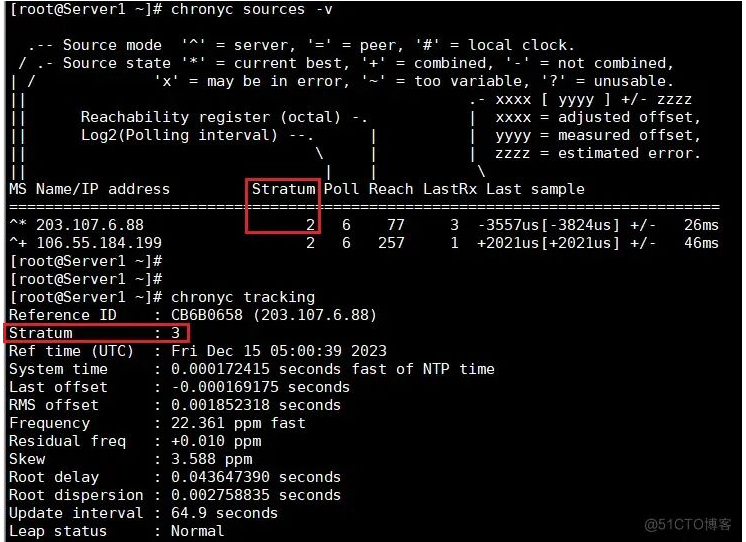
[root@Server1 ~]# chronyc sources MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample =============================================================================== ^* 203.107.6.88 2 6 37 63 +49us[+2956us] +/- 23ms ^- 106.55.184.199 2 6 127 60 +1891us[+1891us] +/- 47ms [root@Server1 ~]# [root@Server1 ~]# chronyc sources -v .-- Source mode '^' = server, '=' = peer, '#' = local clock. / .- Source state '*' = current best, '+' = combined, '-' = not combined, | / 'x' = may be in error, '~' = too variable, '?' = unusable. || .- xxxx [ yyyy ] +/- zzzz || Reachability register (octal) -. | xxxx = adjusted offset, || Log2(Polling interval) --. | | yyyy = measured offset, || | | zzzz = estimated error. || | | MS Name/IP address Stratum Poll Reach LastRx Last sample =============================================================================== ^* 203.107.6.88 2 6 77 3 -3557us[-3824us] +/- 26ms ^+ 106.55.184.199 2 6 257 1 +2021us[+2021us] +/- 46ms [root@Server1 ~]#
chronyc sources输出结果解析:
M
这表示信号源的模式。^表示服务器,=表示对等方,#表示本地连接的参考时钟。
S
此列指示源的状态。
* 表示chronyd当前同步到的源。
+ 表示可接受的信号源,与选定的信号源组合在一起。
– 表示被合并算法排除的可接受源。
?指示已失去连接性或其数据包未通过所有测试的源。它也显示在启动时,直到从中至少收集了3个样本为止。
x 表示chronyd认为是虚假行情的时钟(即,其时间与大多数其他来源不一致)
〜 表示时间似乎具有太多可变性的来源。
Name/IP address
这显示了源的名称或IP地址,或参考时钟的参考ID。
Stratum
这显示了来源的层,如其最近收到的样本中所报告的那样。层1表示一台具有本地连接的参考时钟的计算机。与第1层计算机同步的计算机位于第2层。与第2层计算机同步的计算机位于第3层,依此类推。
Poll
这显示轮询源的速率,以秒为单位的时间间隔的以2为底的对数。因此,值为6表示每64秒进行一次测量。chronyd会根据当前情况自动更改轮询速率。
Reach
这显示了源的可达性寄存器以八进制数字打印。寄存器有8位,并在每个从源接收或丢失的数据包上更新。值377表示从最后八次传输中收到了对所有用户的有效答复。
LastRx
此列显示多长时间前从来源接收到了最后一个好的样本(在下一列中显示)。未通过某些测试的测量将被忽略。通常以秒为单位。字母m,h,d或y表示分钟,小时,天或年。
Last sample
此列显示上次测量时本地时钟与源之间的偏移。方括号中的数字表示实际测得的偏移量。可以用ns(表示纳秒),us (表示微秒),ms(表示毫秒)或s(表示秒)作为后缀。方括号左侧的数字表示原始测量值,已调整为允许此后施加于本地时钟的任何摆度。
+/-指示器后面的数字表示测量中的误差范围。正偏移表示本地时钟位于源时钟之前。
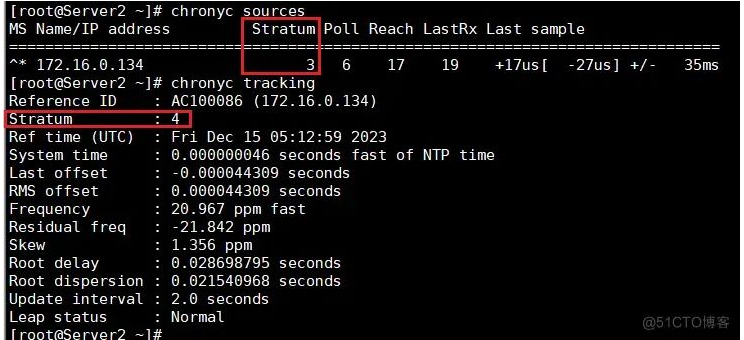
例如:现有时钟服务器time_server:它的层级是2,一台主机node1从time_server同步时间,那么node1主机的层级就是3,以此类推另一台在node1同步时间,那它的层级就是4。
3.3 配置Server2从Server1时间源同步时间
Server1上再次编辑“/etc/chrony.conf”文件:
[root@Server1 ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf # Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project. # Please consider joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html). # pool 2.rocky.pool.ntp.org iburst Server ntp.aliyun.com iburst Server time1.cloud.tencent.com iburst # Record the rate at which the system clock gains/losses time. driftfile /var/lib/chrony/drift # Allow the system clock to be stepped in the first three updates # if its offset is larger than 1 second. makestep 1.0 3 # Enable kernel synchronization of the real-time clock (RTC). rtcsync # Enable hardware timestamping on all interfaces that support it. #hwtimestamp * # Increase the minimum number of selectable sources required to adjust # the system clock. #minsources 2 # Allow NTP client acc ess from local network. #allow 192.168.0.0/16 allow 172.16.0.0/24 # 配置访问规则,仅允许该网络的客户端访问 # Serve time even if not synchronized to a time source. #local stratum 10 local stratum 10 # 即使未同步到时间源,也要提供时间同步服务,当前系统层级为10 # Specify file containing keys for NTP authentication. keyfile /etc/chrony.keys # Get TAI-UTC offset and leap seconds from the system tz database. leapsectz right/UTC # Specify directory for log files. logdir /var/log/chrony # Select which information is logged. #log measurements statistics tracking
重启chronyd服务:
[root@Server1 ~]# systemctl restart chronyd
防火墙放行ntp服务:
[root@Server1 ~]# firewall-cmd --add-service=ntp --permanent success [root@Server1 ~]# firewall-cmd --reload success
Server2上编辑“/etc/chrony.conf”文件:
[root@Server2 ~]# vim /etc/chrony.conf # Use public servers from the pool.ntp.org project. # Please consid er joining the pool (http://www.pool.ntp.org/join.html). # pool 2.rocky.pool.ntp.org iburst # 注释该行,添加下面一行 Server 172.16.0.134 iburst
重启chronyd服务,并设置开机自启:
[root@Server2 ~]# systemctl restart chronyd [root@Server2 ~]# systemctl enable chronyd
查看时间同步状态: